Big O Chart
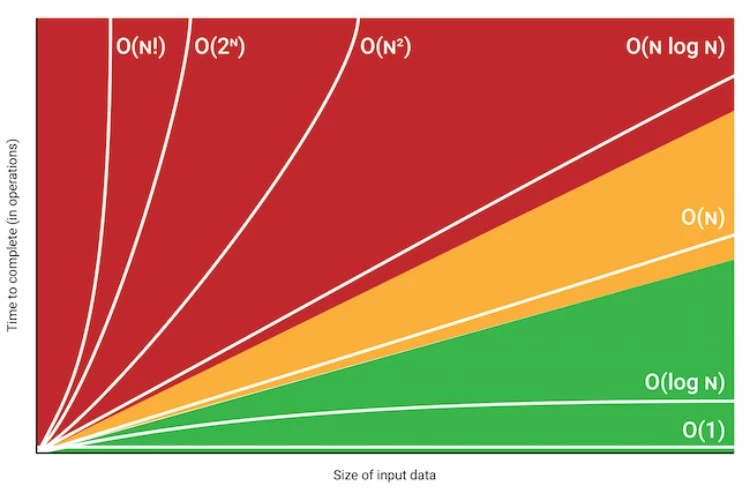
Big O Notation is a mathematical function used in computer science to describe an algorithm’s complexity. It is usually a measure of the runtime required for an algorithm’s execution. But, instead of telling you how fast or slow an algorithm’s runtime is, it tells you how an algorithm’s performance changes with the size of the input (size n).
Here’s some common complexities you’ll find for algorithms:
- Constant time: O(1)
- Logarithmic time: O(logn)
- Linear time: O(n)
- Quadratic time: O(n2)
- Exponential time: O(2n)
- Factorial time: O(n!)
Datastructures Operations (Average case):
| Data Structure | Access | Search | Insertion | Deletion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Array | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) |
| Stack | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) |
| Queue | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) |
| Linked List | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) |
| Hash Table | NA | O(1) | O(1) | O(1) |
| Binary Search Tree | O(log n) | O(log n) | O(log n) | O(log n) |
Array Sorting Algorithms (Average case):
| Algorithm | Time Complexity |
|---|---|
| Bubble Sort | O(n^2) |
| Insertion Sort | O(n^2) |
| Insertion Sort | O(n^2) |
| Quicksort | O(n log(n)) |
| Mergesort | O(n log(n)) |
| Heapsort | O(n log(n)) |
| Bucket Sort | O(n+k) |
| Radix Sort | O(nk) |