Kubernetes Ingress
Kubernetes has become the cornerstone of modern container orchestration, and as applications grow in complexity, managing external access to services within a cluster becomes critical. This is where Kubernetes Ingress comes into play. In this blog post, we’ll explore what Kubernetes Ingress is, it’s benefits, how it works, and provide step-by-step instructions to set up an Ingress controller with multiple services.
What is Kubernetes Ingress?
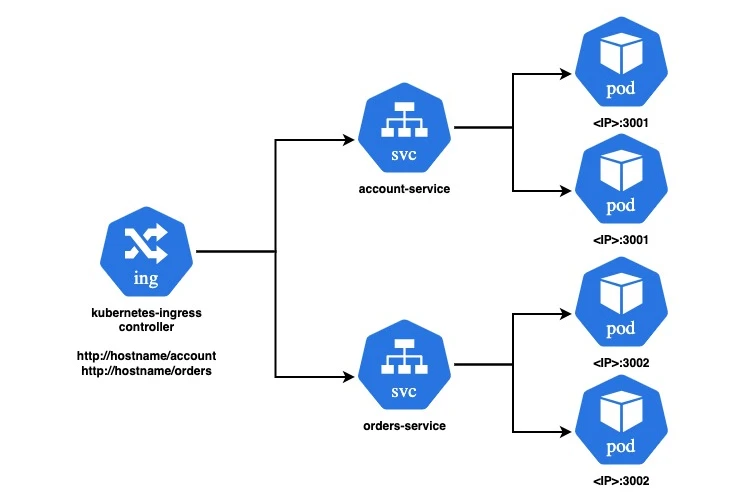
Kubernetes Ingress is an API object that manages external access to services within a Kubernetes cluster, typically HTTP and HTTPS traffic. Ingress can provide load balancing, SSL termination, and name-based virtual hosting, among other features.
Why Use Kubernetes Ingress?
- Simplified Traffic Management: Ingress simplifies the routing of external traffic to internal services, reducing the need for multiple LoadBalancers or NodePorts.
- Centralized Control: It provides a single entry point to your cluster, enabling easier management of traffic routing rules.
- SSL Termination: Ingress can handle SSL/TLS termination, offloading the encryption/decryption process from your services.
- Path-based Routing: You can route traffic to different services based on the request path, which is ideal for microservices architectures.
How Does Kubernetes Ingress Work?
Ingress resources define rules for routing external HTTP/HTTPS traffic to internal services. These rules are processed by an Ingress controller, which is a specialized load balancer running within the cluster. Popular Ingress controllers include NGINX, Traefik, and HAProxy.
Setting Up an Ingress Controller
We’ll use the Minikube setup with Docker and NGINX Ingress Controller to setup the infrastructure. We’ll set up an Ingress controller and configure it to route traffic to two different services based on the URL path. Our setup includes:
- An NGINX Ingress controller.
- Two services, with two pods each.
- Ingress rules to route traffic based on the path.
1. Start Minikube cluster using Docker driver
I am using docker driver with minikube, however other drivers like hyperkit can be also used here.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
minikube start
😄 minikube v1.33.1 on Darwin 10.14.3
✨ Using the docker driver based on existing profile
💨 For improved Docker Desktop performance, Upgrade Docker Desktop to a newer version (Minimum recommended version is 20.10.0, minimum supported version is 18.09.0, current version is 18.09.2)
👍 Starting "minikube" primary control-plane node in "minikube" cluster
🚜 Pulling base image v0.0.44 ...
🔄 Restarting existing docker container for "minikube" ...
🐳 Preparing Kubernetes v1.30.0 on Docker 26.1.1 ...
🔎 Verifying Kubernetes components...
▪ Using image gcr.io/k8s-minikube/storage-provisioner:v5
🌟 Enabled addons: default-storageclass, storage-provisioner
🏄 Done! kubectl is now configured to use "minikube" cluster and "default" namespace by default
2. Enable Ingress Addon in Minikube
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
minikube addons enable ingress
💡 ingress is an addon maintained by Kubernetes. For any concerns contact minikube on GitHub.
You can view the list of minikube maintainers at: https://github.com/kubernetes/minikube/blob/master/OWNERS
💡 After the addon is enabled, please run "minikube tunnel" and your ingress resources would be available at "127.0.0.1"
▪ Using image registry.k8s.io/ingress-nginx/controller:v1.10.1
▪ Using image registry.k8s.io/ingress-nginx/kube-webhook-certgen:v1.4.1
▪ Using image registry.k8s.io/ingress-nginx/kube-webhook-certgen:v1.4.1
🔎 Verifying ingress addon...
🌟 The 'ingress' addon is enabled
3. Verify that the NGINX Ingress controller pods and services are running
1
2
3
4
5
6
kubectl get pods -n ingress-nginx
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
ingress-nginx-admission-create-hn4tw 0/1 Completed 0 5m47s
ingress-nginx-admission-patch-dsks9 0/1 Completed 1 5m47s
ingress-nginx-controller-768f948f8f-5w4kv 1/1 Running 0 5m47s
1
2
3
4
kubectl get service -n ingress-nginx
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
ingress-nginx-controller NodePort 10.96.138.252 <none> 80:32568/TCP,443:32261/TCP 16m
ingress-nginx-controller-admission ClusterIP 10.105.113.227 <none> 443/TCP 16m
4. Install the Ingress Controller
First, we need to install the NGINX Ingress Controller. You can do this using the following YAML configuration ingress.yaml.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: my-ingress
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /account
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: account-service
port:
number: 80
- path: /orders
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: orders-service
port:
number: 80
5. Install accounts service and orders service
We’ll deploy two simple Node.js applications account-service.yaml listening on port 3001 and orders-service.yaml listening on port 3002 having 2 pods each and a service to access the pods. The services will be listening to port 80. These applications will be accessed through different routes in the Ingress configuration.
account-service.yaml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: account-deployment
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: account
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: account
spec:
containers:
- name: account
image: prat1980/node-account-service:v1
ports:
- containerPort: 3001
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: account-service
spec:
selector:
app: account
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 3001
orders-service.yaml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: orders-deployment
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: orders
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: orders
spec:
containers:
- name: orders
image: prat1980/node-orders-service:v1
ports:
- containerPort: 3002
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: orders-service
spec:
selector:
app: orders
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 3002
6. To access your services, you’ll need to use port forwarding.
1
2
3
4
5
kubectl port-forward -n ingress-nginx service/ingress-nginx-controller 8080:80
http://localhost:8080/account
http://localhost:8080/orders
Check logs for troubleshooting
1
kubectl logs -n ingress-nginx deployment/ingress-nginx-controller