MySQL Master Slave Replication (with 0 downtime)
Replication is a critical feature in MySQL that allows you to copy data from one server (master) to one or more servers (slaves/replicas) for high availability, scalability, and redundancy. Setting up MySQL replication without downtime is vital for production environments where continuous availability is a must.
In this guide, we’ll cover how to set up replication for MySQL 5.7 without downtime. This process assumes that the master database is already running and you’re configuring a new slave. Below are the steps.
1. Enable Binary Logging and Configure Master
Edit the master server’s MySQL configuration file (my.cnf or my.ini) to enable binary logging and set a unique server ID.
1
2
3
4
5
6
[mysqld]
server-id=1
log-bin=mysql-bin
binlog-format=ROW
sync_binlog=1
expire_logs_days=7
- log-bin: Enables binary logging, which is necessary for replication.
- server-id: Unique ID for the server in the replication setup.
- binlog-format: Use
ROWfor row-based replication, as it is more robust.
Restart the MySQL server to apply the changes.
1
sudo systemctl restart mysql
2. Create a Replication User on Master
1
2
3
CREATE USER 'replica_user'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'secure_password';
GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'replica_user'@'%';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
3. Login to the server and check the master status
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
show master status;
+------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+
| File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB |
+------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+
| mysql-bin.000001 | 107 | | |
+------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
4. Take a Consistent MySQL dump
To avoid downtime, use a non-blocking backup tool like mysqldump with the –master-data option to create a consistent snapshot of the master.
1
2
mysqldump -u root -p --master-data=2 --single-transaction --skip-lock-tables > master_backup.sql
- –master-data=2: Embeds replication coordinates (binary log file and position) in the dump file.
- –single-transaction: Ensures a consistent dump.
- –skip-lock-tables: Avoid locking tables during the dump process.
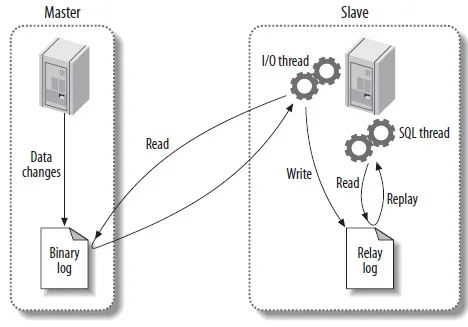
5. Configure the Slave
On the slave server, update the MySQL configuration to set a unique server ID and enable replication settings.
1
2
3
4
5
[mysqld]
server-id=2
relay-log=relay-log
log-slave-updates=1
read-only=1
- relay-log: Store events read from the master server’s binary log, allowing a replica server to apply these events.
- log-slave-updates=1: The replica writes updates that are received from a master to its own binary logs.
- read-only=1: Convert the database into a READ-ONLY state.
Restart the MySQL server to apply the changes.
1
sudo systemctl restart mysql
6. Restore the Backup on the Slave
1
mysql -u root -p < master_backup.sql
7. Set Up Replication in Slave server
Check the MASTER_LOG_FILE and MATER_LOG_POS in the mysqldump file.
1
head dump.sql -n80 | grep "MASTER_LOG_POS"
Use the information to configure the Slave
1
2
3
4
5
6
CHANGE MASTER TO
MASTER_HOST = '172.17.0.2',
MASTER_USER = 'replica_user',
MASTER_PASSWORD = 'password',
MASTER_LOG_FILE = 'mysql-bin.000001',
MASTER_LOG_POS = 107;
Star the replication process in the Slave
1
START SLAVE;
8. Verify the status of Replication
You should see “Slave_IO_Running” and “Slave_SQL_Running” as “Yes” if the replication is working correctly.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
SHOW SLAVE STATUS \G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Slave_IO_State: Waiting for master to send event
Master_Host: 172.17.0.2
Master_User: replica_user
Master_Port: 3306
Connect_Retry: 60
Master_Log_File: mysql-bin.000001
Read_Master_Log_Pos: 107
Relay_Log_File: relay-bin.000001
Relay_Log_Pos: 266
Relay_Master_Log_File: mysql-bin.000001
Slave_IO_Running: Yes
Slave_SQL_Running: Yes
...
With the above settings we can setup a 2 node MySQL Master-Slave Replication setup for availability and performance.
The configuration has been tested for MySQL 5.7 please use it wisely for later versions.