Scaling PHP to Millions of Users

PHP is a popular server-side scripting language known for its ease of use and flexibility. However, as your web application gains traction and attracts millions of users, your PHP codebase and infrastructure may start to experience performance bottlenecks. Scaling PHP to accommodate such a large user base requires careful planning, optimization, and utilization of the right tools. In this blog post, we’ll explore essential strategies to scale PHP to millions of users and ensure your application remains fast, reliable, and scalable.
1. Optimize Your PHP Code
- Optimize loops and conditionals: Use efficient algorithms and avoid nested loops wherever possible.
- Profiling and debugging: Identify and fix bottlenecks using profiling tools like Xdebug or XHProf.
- Session storage: For Session storage consider using a distributed session store like Redis to improve session handling and avoid session-related bottlenecks.
- Optimize Database Queries: Continuously monitor and optimize your database queries to ensure they run efficiently. Use database indexing, denormalization, and other techniques to improve query performance.
- Optimize JavaScript and CSS: Minimize and concatenate your JavaScript and CSS files to reduce the number of requests made to the server, improving page load times.
- Content Compression: Implement content compression using gzip or Brotli to reduce the size of data sent from the server to the client, improving overall performance.
- Static Analysis Tools: Incorporate static analysis tools like Sonarqube to identify bugs and potential issues early in the development process.
- Database Connection Pooling: Utilize database connection pooling to efficiently manage and reuse database connections, reducing the overhead of establishing new connections.
- Feature Flags: Feature flags are a software development concept that allow you to enable or disable a feature without modifying the source code or requiring a redeploy.
- Asynchronous Processing: For tasks that are not required to be completed immediately, consider using asynchronous processing. Technologies like Gearman, RabbitMQ or Apache Kafka allow you to decouple tasks from the main request-response cycle, improving the overall performance of your application.
- Microrepos: Consider breaking down your application into smaller, independent services. This allows you to scale individual components independently, making it easier to handle varying workloads and reducing the impact of failures in one service on the whole application.
- PHP Version: Always upgrade to the latest version of PHP. Newer versions are always faster then it’s predecessor.
2. Optimise your PHP Configuration (PHP-FPM)
Tune PHP-FPM settings to match the available resources and the expected workload of your application.
Worker Processes and Pools
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
pm = dynamic
pm.max_children = 1000 ; Adjust this based on your server's resources and expected traffic
pm.start_servers = 20 ; The number of child processes to create on startup
pm.min_spare_servers = 10 ; Minimum number of idle processes
pm.max_spare_servers = 50 ; Maximum number of idle processes
pm.process_idle_timeout = 10s ; How long an idle process will stay alive
pm.max_requests = 500 ; Recycle processes after a certain number of requests to prevent memory leaks
Resource Limits
1
2
3
pm.max_requests = 500 ; Recycle processes after a certain number of requests to prevent memory leaks
request_terminate_timeout = 60s ; Maximum time a request is allowed to run
request_slowlog_timeout = 30s ; Time to log slow requests
PHP-FPM Logging
1
2
access.log = /var/log/php-fpm/access.log
slowlog = /var/log/php-fpm/slow.log
Other Recommended Tweaks
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
pm.status_path = /status ; Enable the status page for monitoring PHP-FPM status
; Fine-tune PHP settings based on your application's requirements
php_admin_value[memory_limit] = 256M
php_admin_value[max_execution_time] = 30
; Disable realpath cache if you're using opcache
php_admin_value[opcache.enable] = 0
3. Use of caching
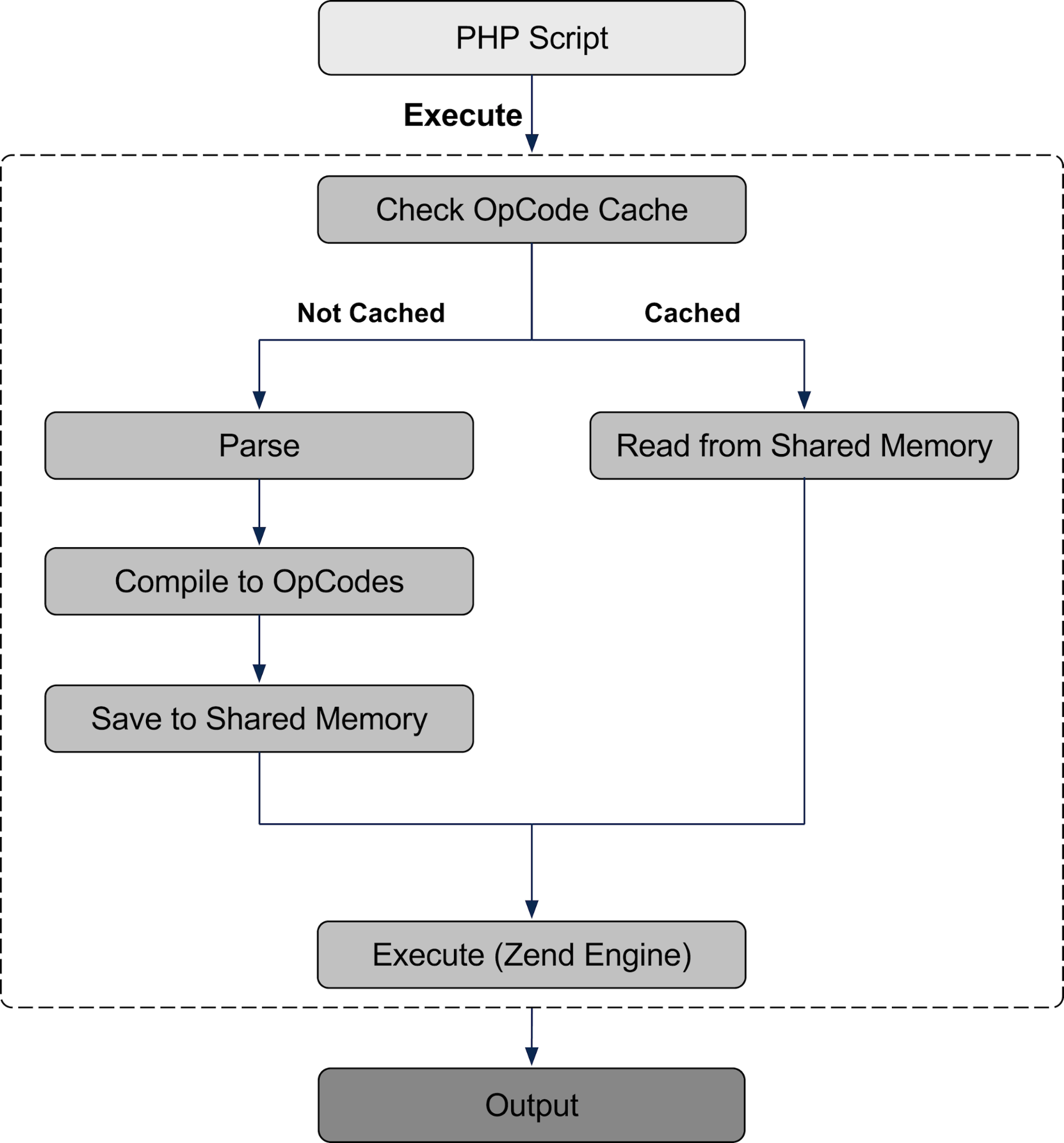
- Enable opcode caching: PHP opcode caches like OPcache store precompiled scripts in memory, reducing the need for PHP to parse and compile code on every request.
- Caching: Implement database query caching to reduce the load on the database and improve response times. Consider tools like Redis or Memcache.
- Use Content Caching: Implementing full-page caching can significantly reduce the load on your PHP servers. Tools like Varnish or Nginx FastCGI caching can cache entire pages and serve them directly to users without invoking PHP.
4. Use a Load Balancer to scale horizontally
When dealing with millions of users, a single web server may not be sufficient to handle the incoming traffic. Implement a load balancer to distribute incoming requests across multiple web servers, improving response times and ensuring high availability.
5. Scale Your Database
As user numbers grow, the database can become a major bottleneck. Consider the following approaches to scale your database:
- Tuning: Tune your MySQL server for InnoDB vs MyIASM tables.
- Master-slave replication: Use a master database for writes and replicate the data to multiple read-only slave databases for better read performance.
- Database sharding: Split your database into smaller, manageable partitions to distribute the data across multiple servers.
6. Use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
Offloading static assets like images, CSS, and JavaScript files to a CDN can significantly reduce the load on your PHP servers. CDNs cache content in multiple locations worldwide, providing faster access to users regardless of their geographical location.
7. Monitoring
Consider monitoring of the PHP application to identify potential bottlenecks and fix them continuously.